- Article
The Impact of Rheological Characteristics on the Swallowing Dynamics of Xanthan Gum-Based Thickeners
- Yuki Hayakawa,
- Jumpei Okawa and
- Kazuhiro Hori
- + 6 authors
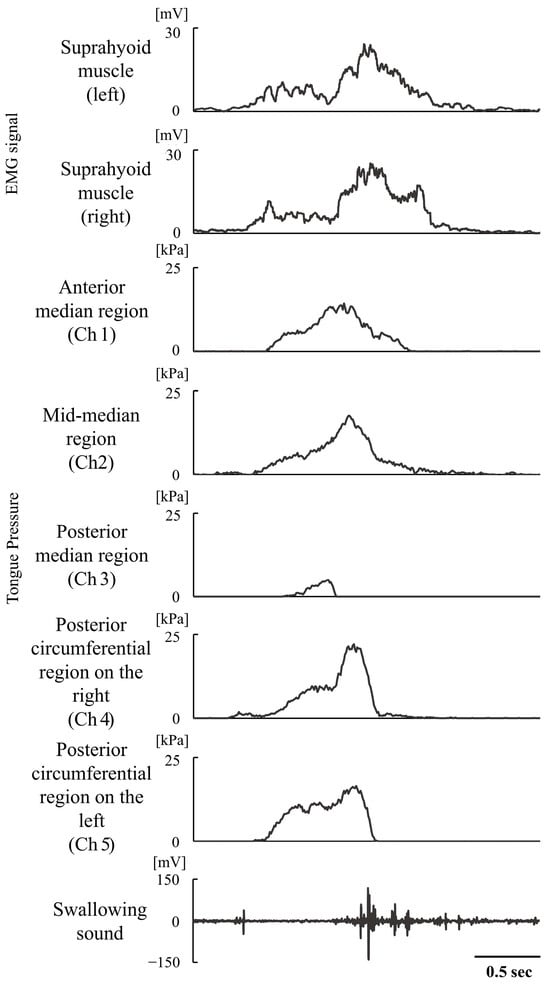
Xanthan gum-based thickeners are commonly used to treat dysphagic patients. Their rheological properties, such as shear-thinning, extension, and thixotropy, contribute to swallowing safety. However, the influence of rheological variations on swallowing dynamics remains unclear. This study investigated the impact of variations in the rheological properties of xanthan gum-based thickeners on swallowing dynamics, specifically tongue pressure, suprahyoid muscle activity, and swallowing sounds. Shear rheology, extensional viscosity, and 3-interval thixotropy tests were conducted on three commercial thickener solutions standardized to a 400 mPa·s viscosity at a 50 s−1 shear rate. Twenty healthy volunteers (11 females, 24.6 ± 2.4 years) participated in this study, during which tongue pressure, suprahyoid muscle activity, and swallowing sounds were measured while swallowing 15 mL samples. The first thickener exhibited reduced shear viscosity at 300 s−1, higher thixotropy, and shorter swallowing sound duration, suggesting a shortened pharyngeal transit time. The second showed prolonged filament breakage time and higher tongue pressure in the posterior-median region of the palate, leading to increased tongue activity during swallowing. The third exhibited lower extensional viscosity, different muscle activity than the second, and longer duration of swallowing sound than the first. These results suggest that rheological property variations in xanthan gum-based thickeners influence swallowing dynamics in healthy individuals.
28 January 2026